Novel biomarker for Antibody Drug Conjugate

The current use of precision medicine improves specificity of cancer treatment, but not in all patients. Better predictive markers for clinical response are therefore warranted.
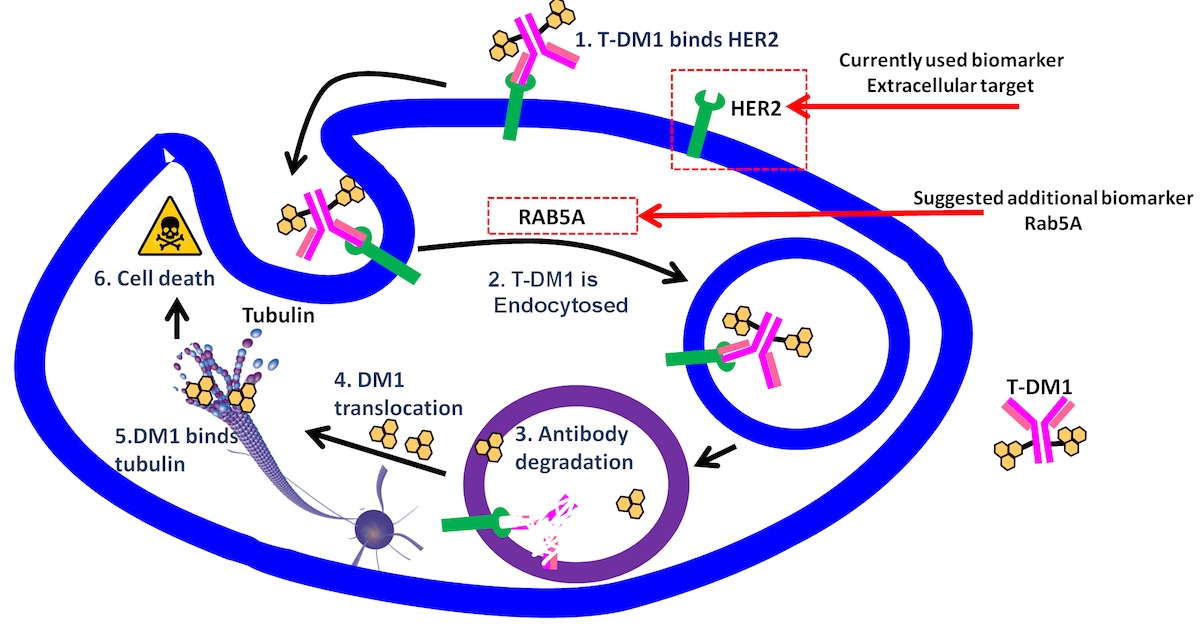
The study "RAB5A expression is a predictive biomarker for trastuzumab emtansine in breast cancer", led by Dr Anette Weyergang, is the first demonstrating that proteins involved in intracellular transport can be utilized as biomarkers for ADC treatment. The manuscript has been published in Nature Communications.
The study is focused on antibody drug conjugates (ADCs), an up and coming drug class within cancer therapeutics.
In this study the authors first showed a high correlation between Rab5A, a protein involved in endocytosis, and T-DM1, an HER2 targeted ADC in a cell line panel. The result was validated in a clinical cohort from the I-SPY2 study in collaboration with Laura Esserman and her research team at UCSF, and finally verified in an independent clinical cohort from the Kamilla study at OUS.
Overall, the results of this study imply that current and future ADC treatment will benefit from the incorporation of biomarkers reflecting uptake and intracellular transport.
The project is admitted to the SPARK innovation program.
Links:
The paper:
RAB5A expression is a predictive biomarker for trastuzumab emtansine in breast cancer
Olav Engebraaten, Christina Yau, Kristian Berg, Elin Borgen, Øystein Garred, Maria E. B. Berstad, Ane S. V. Fremstedal, Angela DeMichele, Laura van ’t Veer, Laura Esserman & Anette Weyergang
Nature Communications volume 12, Article number: 6427 (2021)
Article in Dagens Medisin:
Norske forskere kan ha funnet ny biomarkør for behandling av brystkreft
Anette Weyergang's project group - Recombinant Light Activated Therapeutics
Department of Radiation Biology
