The development of breast cancer is a complex phenomenon that requires a number of genes and molecular pathways. The disease is a synergistic interplay of genes and pathways and only a combination of drugs that targets these genes and pathways will be effective. Breast cancer patients are usually treated with a combination of different modalities spanning from surgery and radiation treatment to chemotherapy, hormonal therapy and targeted treatment depending of type and stage of disease. The degree to which the treatment is tailored to the individual patient depends on the type of treatment.
We, in our group study how the epigenetic characteristics of the tumor influence the tumors response to therapy. Anthracyclines and taxanes represent the most active agents used in breast cancer. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy regimens have been extensively used in the treatment of locally advanced breast cancer, before surgery to allow surgical resection/mastectomy with acceptable margins, and to ultimately extend survival of the patients. Despite the improved results obtained by more aggressive and individual response tailored therapy, patients with large tumor still have a less favourable outcome compared to patients diagnosed with smaller tumors. Whether antiangiogenic treatment strategies as bevacizumab may improve the tumor response and eventually the prognosis for these patients, is still unknown.
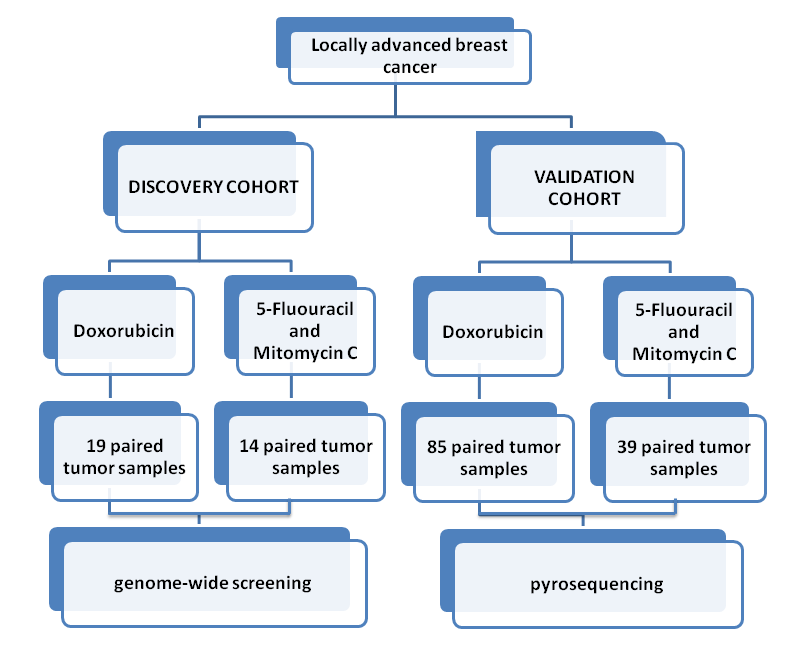
Figure 1.Study design. FromDNA methylation status of key cell-cycle regulators such as CDKNA2/p16 and CCNA1 correlates with treatment response to doxorubicin and 5-fluorouracil in locally advanced breast tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 2014 Dec 15;20(24):6357-66. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-0297. Epub 2014 Oct 7. PMID:25294903 DOI:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-0297
DNA methylation patterns as a potential marker for treatment response
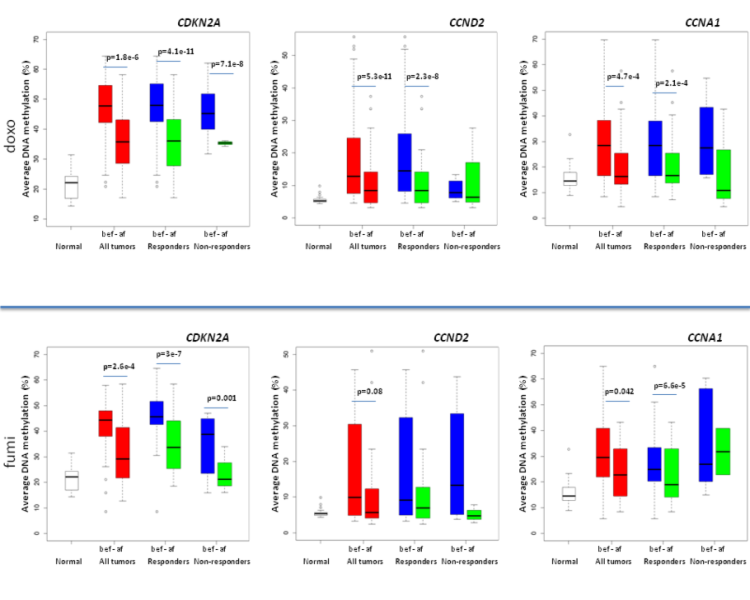
Figure 2. Average percentage of DNA methylation levels for CDKN2A, CCND2 and CCNA1 gene in doxorubicin and 5-fluorouracil Mitomycin C treated breast cancers. For each gene difference in methylation between all samples before/after, between responders before/after and between non-responders before/after and normal samples are shown. From DNA methylation status of key cell-cycle regulators such as CDKNA2/p16 and CCNA1 correlates with treatment response to doxorubicin and 5-fluorouracil in locally advanced breast tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 2014 Dec 15;20(24):6357-66. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-0297. Epub 2014 Oct 7. PMID:25294903 DOI:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-0297
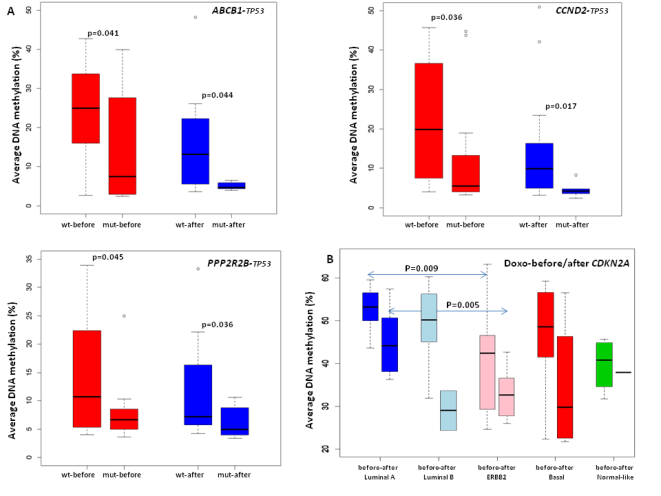
Figure 3. A) Boxplots illustrating significant association between methylation status and TP53 mutation status. For each gene difference in methylation between wild type and TP53 mutated tumors before and after treatment is given. B) Boxplots illustrating the differential methylation of CDKN2A between different molecular subtypes before and after treatment with doxorubicin. From DNA methylation status of key cell-cycle regulators such as CDKNA2/p16 and CCNA1 correlates with treatment response to doxorubicin and 5-fluorouracil in locally advanced breast tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 2014 Dec 15;20(24):6357-66. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-0297. Epub 2014 Oct 7. PMID:25294903 DOI:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-0297
How immune system responds to time course anti angiogenic treatment in
breast cancer patients- assessed as serum cytokines levels?
Study plan:
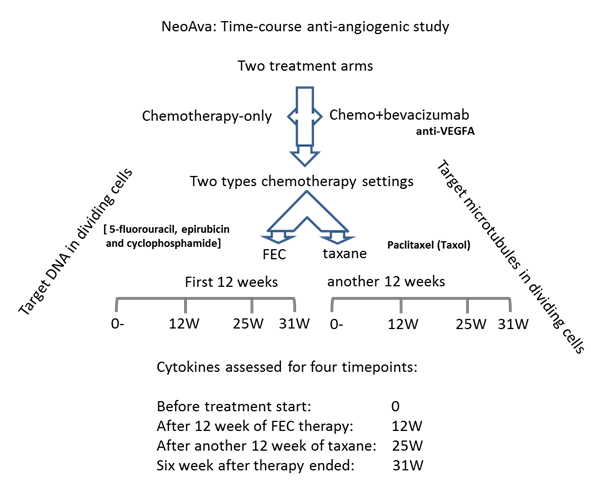
Figure 4. Study design.
Anti-angiogenic drug bevacizumab lowered the concentrations of its target VEGF-A to the least when combined with anthracycline-containing regimen FEC as neo-adjuvant chemotherapy in this breast cancer time course treatment study. Anti- VEGF-A therapy not only lowered the serum levels of VEGF-A but also diminished the levels of direct or indirect regulators of VEGF-A.
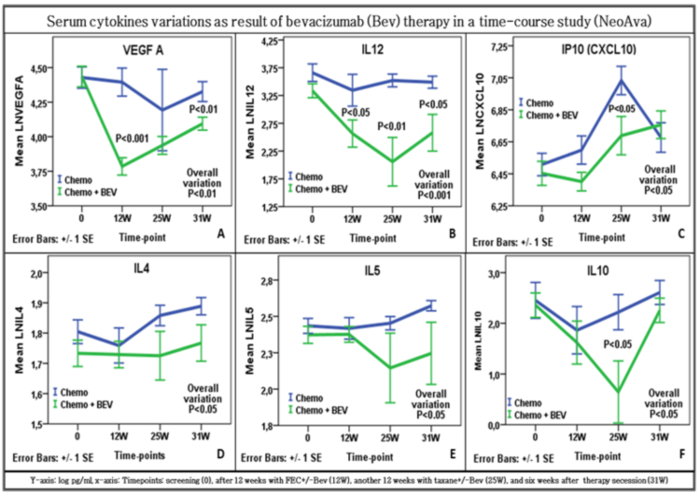
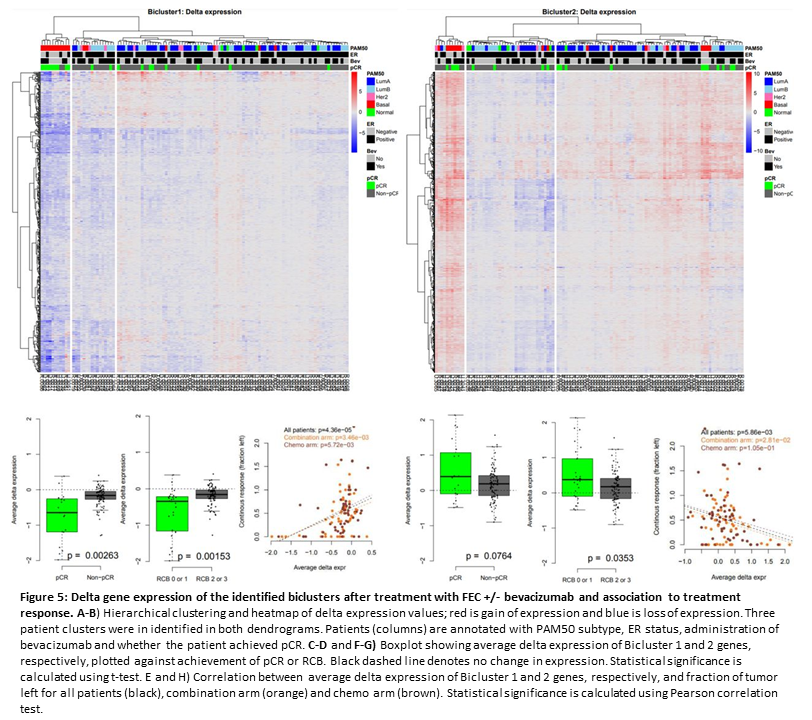
Figure 5. Cytokines levels assessed at four timepoints in breast cancer patients from two treatment arms: control or chemotherapy-only (chemo) arm, and chemotherapy plus bevacizumab (Bev) arm of treatment (unpublished).
An integrated ‘omics approach highlights the role of epigenetic events to explain and predict response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy and bevacizumab
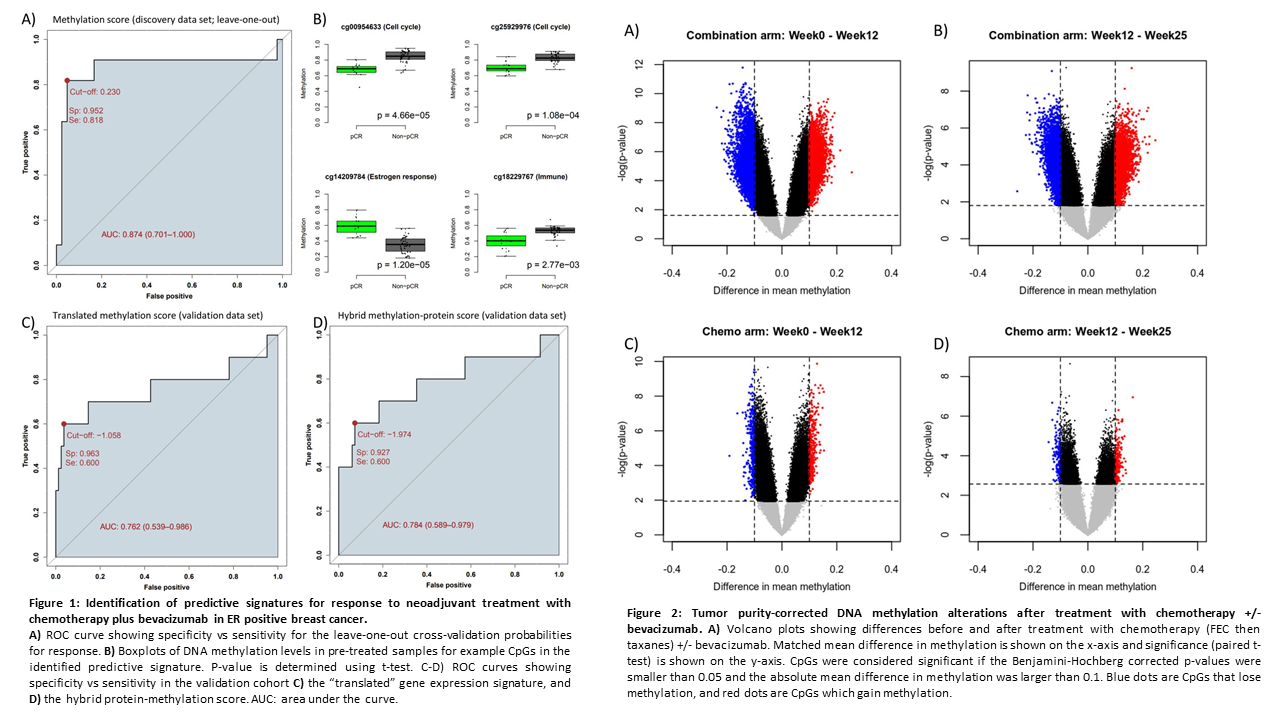
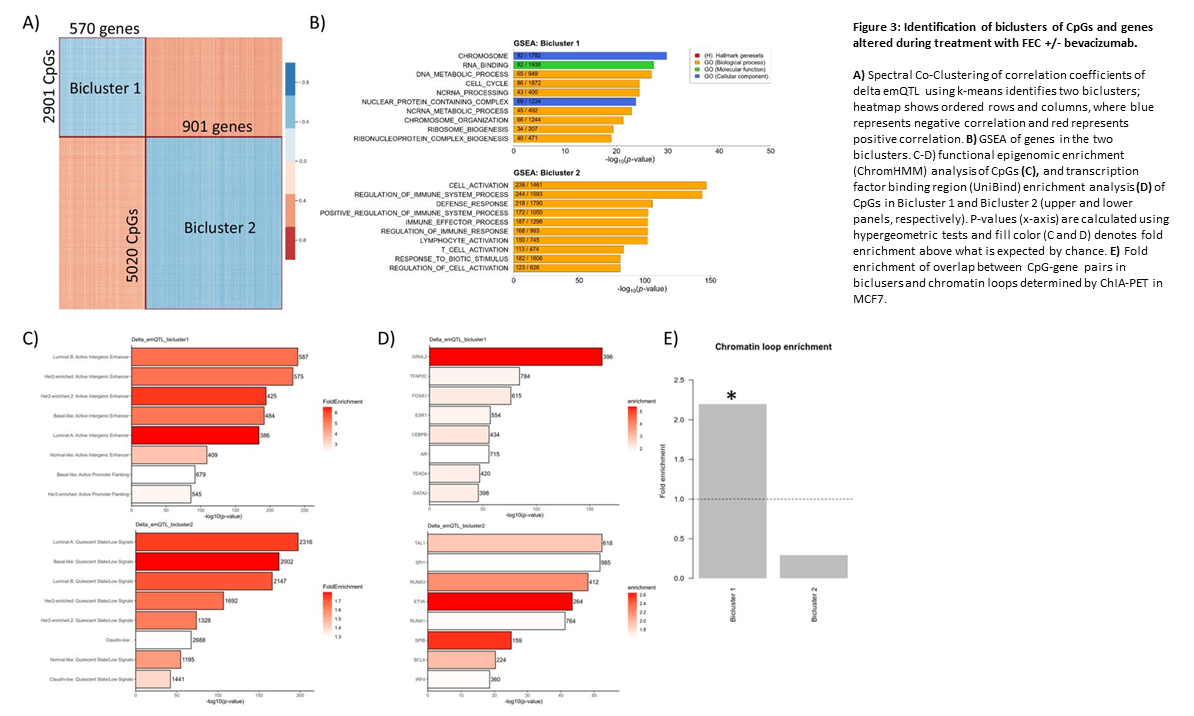
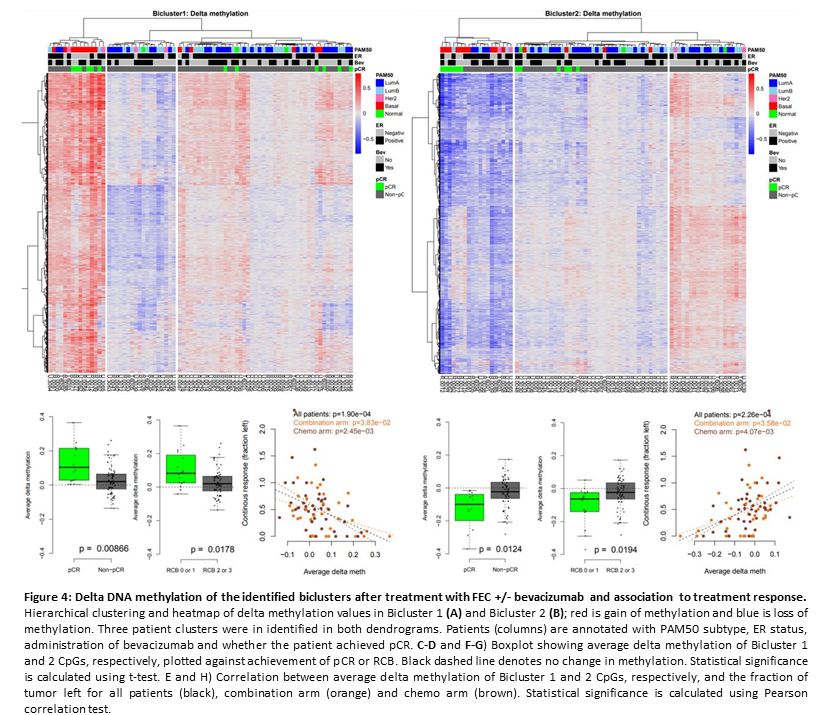
Project members: Jovana Klajic , Grethe I. G. Alnæs, Thomas Fleischer, Shakila Jabeen,
Former members: Hege Edvardsen, Silje Nord, Tone Olsen, Ann Rita Halvorsen, Surendra Kumar
Phd Thesis from project:
1. Jovana Klajic 17.06.2014; Title of the thesis: From normal breast to invasive carcinoma: DNA methylation profiling of stage and response to chemotherapy.
External collaborators:
- Clinical collaborators: Bjørn Naume, JOlav Engebråten, Jon Amund Kyte, Per Eystein Lønning, Jurgen Geisler
- Peter Fasching, Univ. Erlanden, http://www.frauenklinik.uk-erlangen.de/kontakt/visitenkarte/vk/peter-andreasfasching/1965/
- Suzette Delaloge, Inst Gustave Roussy, https://www.gustaveroussy.fr/en/content/cancer-du-sein-equipe
Recent publications:
1. DNA methylation status of key cell-cycle regulators such as CDKNA2/p16 and CCNA1 correlates with treatment response to doxorubicin and 5-fluorouracil in locally advanced breast tumors.
Clin Cancer Res. 2014 Dec 15;20(24):6357-66. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-0297. Epub 2014 Oct 7. PMID:25294903 DOI:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-0297
2. Differential DNA methylation analysis of breast cancer reveals the impact of immune signaling in radiation therapy.
Int J Cancer. 2014 Nov 1;135(9):2085-95. doi: 10.1002/ijc.28862. PMID:24658971
3. DNA methylation profiling in doxorubicin treated primary locally advanced breast tumours identifies novel genes associated with survival and treatment response.
Mol Cancer. 2010 Mar 25;9:68. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-9-68. PMID:20338046
