Abrahamsen and Stenmark write about growth signalling in Science

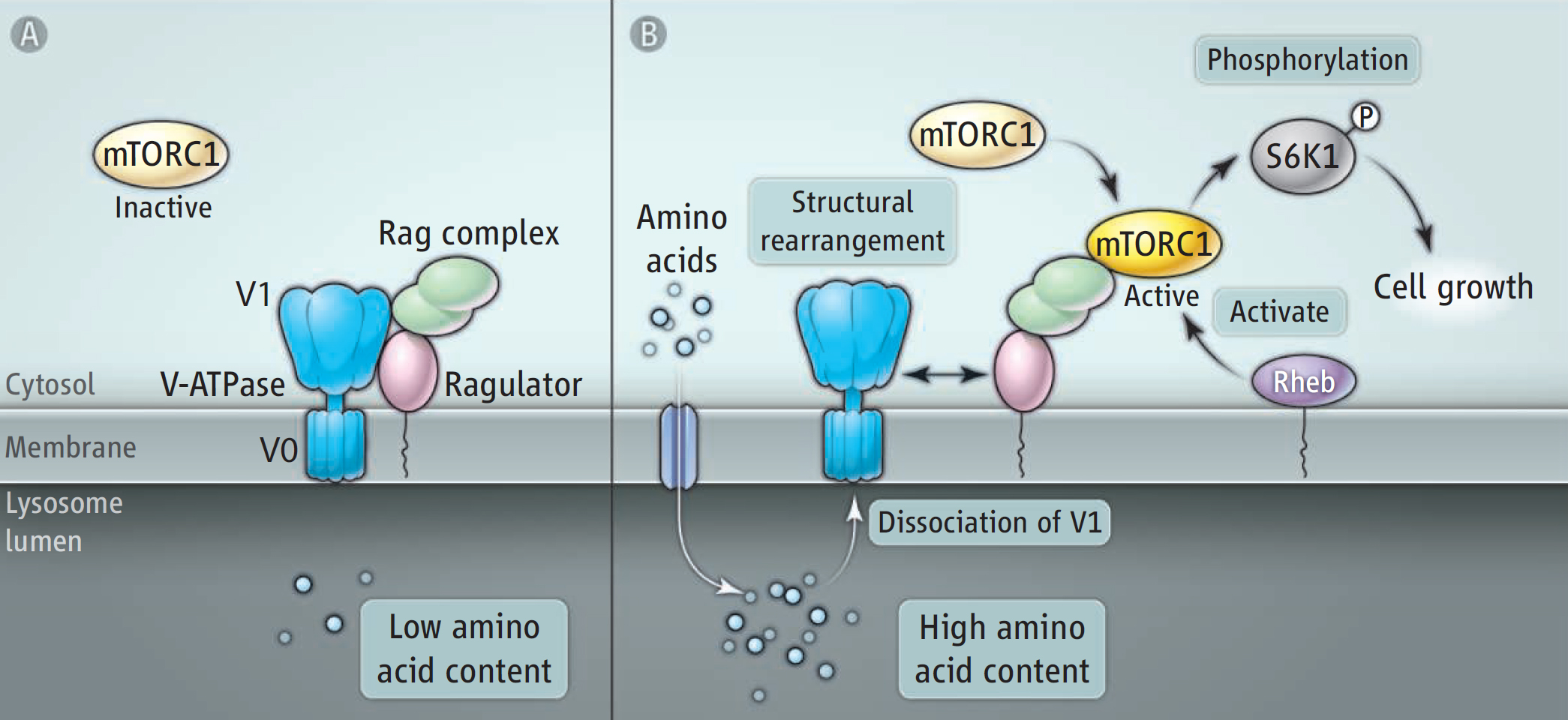
A fundamental property of the cells of our body is the ability to sense whether nutrients are scarce or abundant so that appropriate anabolic or catabolic programmes can be initiated. Such sensing is by no means unique to human cells, this basic property is conserved from unicellular eukaryotes such as yeast, and so is the key sensor of nutrient status, target of rapamycin (TOR). TOR is an enzyme capable of phosphorylating a subset of proteins with key roles in cell growth and metabolism. In mammalian cells, TOR engages together with accessory proteins to form mammalian TOR complex 1 (mTORC1), and major effort has been taken to delineate how various environmental inputs can regulate this central growth coordinator. It has been known for a long time that amino acids are potent activators of mTORC1, but one of the unanswered questions has been how mTORC1 senses amino acids within the cell. In the Science Perspective, Abrahamsen and Stenmark discuss a recent paper by Zoncu et al. which reports that amino acids are sensed inside the lumen of lysosomes, the main degradative organelles in the cell. The sensing mechanism is an intriguing one: high amino acid levels within the lysosome alter the structural composition of a lysosomal proton pump, which mediates recruitment of mTORC1 to the cytoplasmic face of the lysosomal membrane to provide proximity between mTORC1 and its activator Rheb. This in turn causes activation of mTORC1.
The central role of mTORC1 as a coordinator of nutrient responses is accompanied by a great interest in targeting mTORC1 pharmacologically. mTORC1 inhibitors are already being used clinically against certain cancers. The recent advance in our understanding of how mTORC1 is activated is therefore good news because it provides us with new strategies for targeting TOR signalling in cancer therapy.
Links:
Science 334, 611 (2011);
Hilde Abrahamsen, et al.
Growth Signaling from Inside
Download PDF
Home page of Harald Stenmark's group - Intracellular Communication