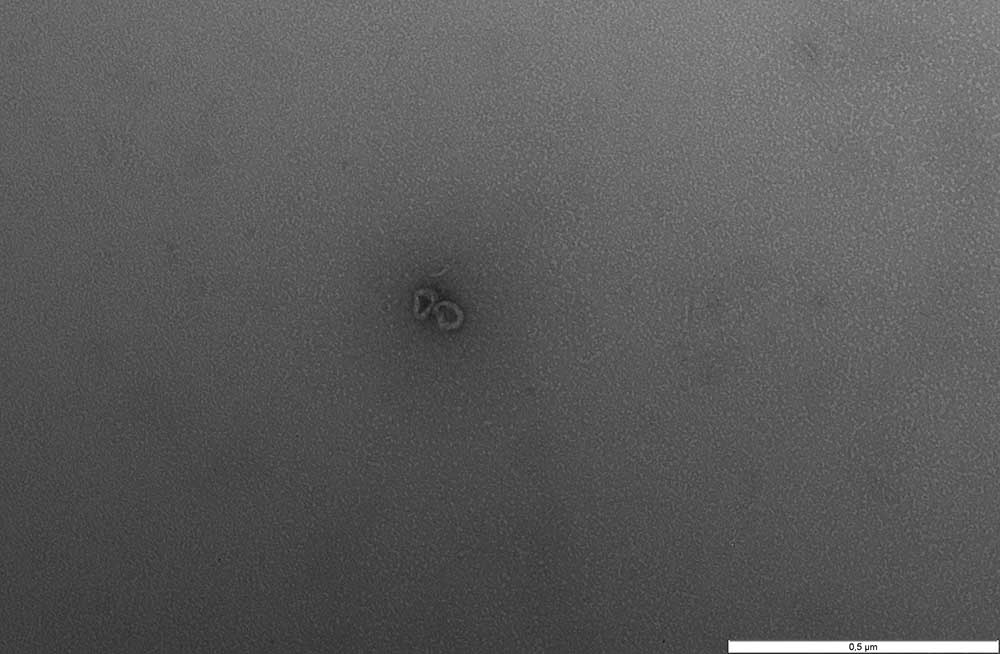
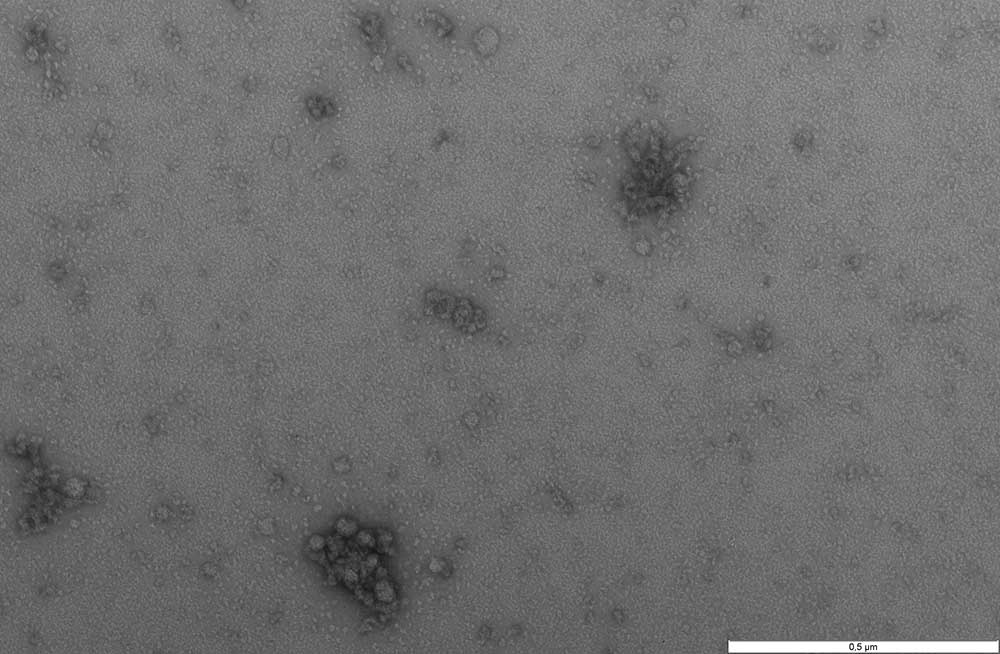
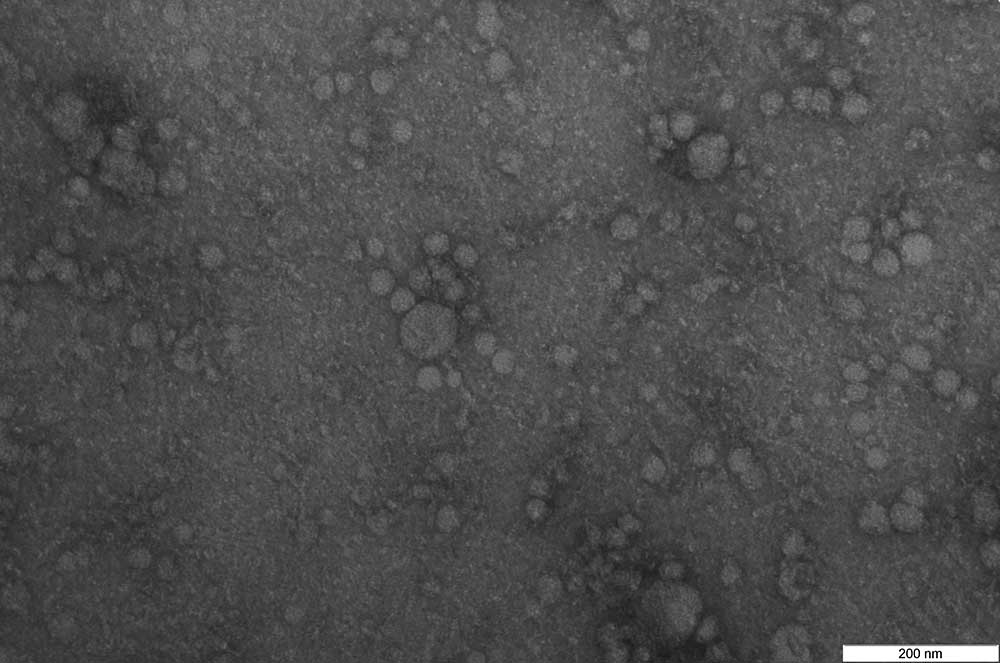
Negative stain
Negative staining is a method for studying particulate specimens. In principle, the specimen such as extra cellular vesicles (EVs) are surrounded by heavy metal atoms that act as an electron barrier. Because the electron beam can pass through the low electron density of the specimen but not through the metallic background, the result is negative staining: a light specimen against dark background. We commonly employ 4% Uranyl acetate in water and the duration of staining varies according to specimen types.
 |
 |
 |
