RSA is the science of obtaining reliable 3D in vivo measurements from stereographic x-ray images (Karrholm et al. 1997). This high accuracy measuring method was developed by Selvik in Sweden 2. It is a complicated and time-consuming method, which yields high quality information with little radiation for the patients. RSA is the golden standard for analysing implants in bone and joints, healing of bone and ligaments and joint movement 3, 4. The technique requires small tantalum balls (0.5-1.0 mm Ø) to be implanted in the bone or they can be attached to the implant of interest (Figure 1). Two radiographs are taken simultaneously (stereogrammetry) with the films in a cage that has reference tantalum balls for precise determination of the 3-dimensional position (these coordinates are known) (Figure 2). The radiographs are then computer-analysed, and from the position of the known reference markers in the cage the position of the markers in the patient can be precisely determined. By serial examinations the movement of segments (a group of markers in the bone or attached to an implant which constitutes a rigid body) can be followed, for instance the movement of prostheses in the bone, or the movement of the bone ends during fracture healing. Movements can be measured as translations along the three axes, or as rotations around the three axes (Figure 3) For quality control of implants in the human body (prosthesis and osteosyntesis) RSA is the only precise method available. When the new bone cement Boneloc was introduced the Norwegian arthroplasty register needed 1100 patients before it could be proven to be an inferior cement due to a higher revision rate than for patients operated with regular bone cement 5. With RSA only 30 patients were included in the study that already after 6 months showed that Boneloc cemented implants were more unstable than those with conventional bone cement 6. Early instability is predictive of later loosening of implants 7. If Boneloc had been studied with RSA before it had been released onto the market, thousands of patients would have been spared from early revision. | 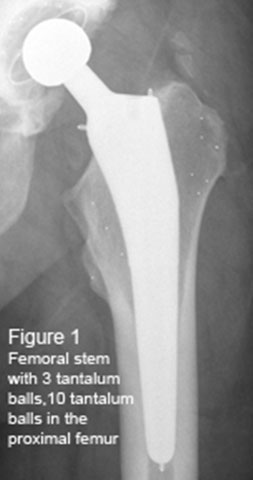
|